Description
You are given an integer n and an undirected, weighted tree rooted at node 0 with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. This is represented by a 2D array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates an edge from node ui to vi with weight wi.
The weighted median node is defined as the first node x on the path from ui to vi such that the sum of edge weights from ui to x is greater than or equal to half of the total path weight.
You are given a 2D integer array queries. For each queries[j] = [uj, vj], determine the weighted median node along the path from uj to vj.
Return an array ans, where ans[j] is the node index of the weighted median for queries[j].
Example 1:
Input: n = 2, edges = [[0,1,7]], queries = [[1,0],[0,1]]
Output: [0,1]
Explanation:
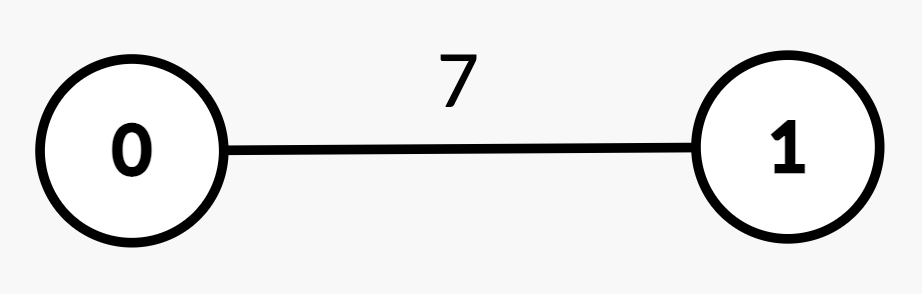
| Query | Path | Edge Weights | Total Path Weight | Half | Explanation | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[1, 0] | 1 → 0 | [7] | 7 | 3.5 | Sum from 1 → 0 = 7 >= 3.5, median is node 0. | 0 |
[0, 1] | 0 → 1 | [7] | 7 | 3.5 | Sum from 0 → 1 = 7 >= 3.5, median is node 1. | 1 |
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,2],[2,0,4]], queries = [[0,1],[2,0],[1,2]]
Output: [1,0,2]
Explanation:
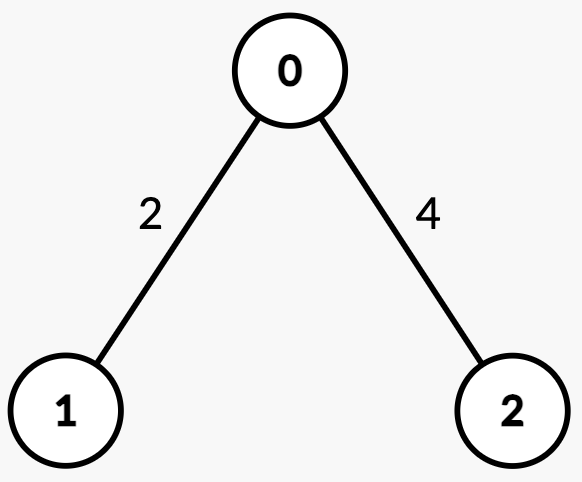
| Query | Path | Edge Weights | Total Path Weight | Half | Explanation | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[0, 1] | 0 → 1 | [2] | 2 | 1 | Sum from 0 → 1 = 2 >= 1, median is node 1. | 1 |
[2, 0] | 2 → 0 | [4] | 4 | 2 | Sum from 2 → 0 = 4 >= 2, median is node 0. | 0 |
[1, 2] | 1 → 0 → 2 | [2, 4] | 6 | 3 | Sum from 1 → 0 = 2 < 3.Sum from 1 → 2 = 2 + 4 = 6 >= 3, median is node 2. | 2 |
Example 3:
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,2],[0,2,5],[1,3,1],[2,4,3]], queries = [[3,4],[1,2]]
Output: [2,2]
Explanation:
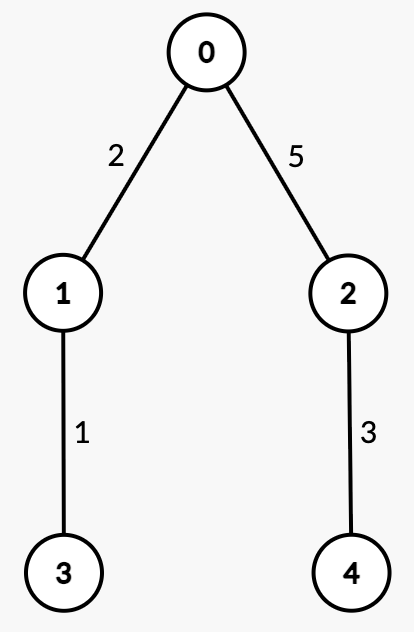
| Query | Path | Edge Weights | Total Path Weight | Half | Explanation | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[3, 4] | 3 → 1 → 0 → 2 → 4 | [1, 2, 5, 3] | 11 | 5.5 | Sum from 3 → 1 = 1 < 5.5.Sum from 3 → 0 = 1 + 2 = 3 < 5.5.Sum from 3 → 2 = 1 + 2 + 5 = 8 >= 5.5, median is node 2. | 2 |
[1, 2] | 1 → 0 → 2 | [2, 5] | 7 | 3.5 |
Sum from | 2 |
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i] == [ui, vi, wi]0 <= ui, vi < n1 <= wi <= 1091 <= queries.length <= 105queries[j] == [uj, vj]0 <= uj, vj < n- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution
Python3
class Solution:
def findMedian(self, N: int, edges: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
M = N.bit_length() + 1
graph = defaultdict(list)
for a, b, w in edges:
graph[a].append((b, w))
graph[b].append((a, w))
parent = [[0] * M for _ in range(N)]
weights = [0] * N
d = [0] * N
def dfs(node, prev, depth, w):
parent[node][0] = prev
d[node] = depth
weights[node] = w
for adj, w2 in graph[node]:
if adj != prev:
dfs(adj, node, depth + 1, w + w2)
dfs(0, 0, 0, 0)
# binary lifting
for power in range(1, M):
for node in range(N):
parent[node][power] = parent[parent[node][power - 1]][power - 1]
def lca(a, b):
if d[a] > d[b]:
a, b = b, a
# let a and b jump to the same depth
diff = d[b] - d[a]
for p in range(M):
if diff & (1 << p):
b = parent[b][p]
if a == b: return a
for p in range(M - 1, -1, -1):
if parent[a][p] != parent[b][p]:
a = parent[a][p]
b = parent[b][p]
return parent[a][0]
def pathSum(a, b, ancestor):
return weights[a] + weights[b] - 2 * weights[ancestor]
res = []
for a, b in queries:
if a == b:
res.append(a)
continue
oa, ob = a, b
ancestor = lca(a, b)
w = pathSum(a, b, ancestor)
median = w / 2
ok = False
if pathSum(a, ancestor, ancestor) >= median:
k = 0
while True:
p = parent[a][k]
if pathSum(oa, p, p) >= median:
if k == 0:
res.append(p)
ok = True
break
else:
a = parent[a][k - 1]
k = -1
k += 1
if ok: continue
offset = pathSum(a, ancestor, ancestor)
k = 0
while True:
p = parent[b][k]
if pathSum(ancestor, p, ancestor) + offset < median:
if k == 0:
break
else:
b = parent[b][k - 1]
k = -1
k += 1
res.append(b)
return resC++
int n, l;
vector<vector<array<int, 2>>> adj;
int timer;
vector<int> tin, tout;
vector<vector<int>> up;
void dfs(int v, int p)
{
tin[v] = ++timer;
up[v][0] = p;
for (int i = 1; i <= l; ++i)
up[v][i] = up[up[v][i-1]][i-1];
for (auto& [u, w] : adj[v]) {
if (u != p)
dfs(u, v);
}
tout[v] = ++timer;
}
bool is_ancestor(int u, int v)
{
return tin[u] <= tin[v] && tout[u] >= tout[v];
}
int lca(int u, int v)
{
if (is_ancestor(u, v))
return u;
if (is_ancestor(v, u))
return v;
for (int i = l; i >= 0; --i) {
if (!is_ancestor(up[u][i], v))
u = up[u][i];
}
return up[u][0];
}
void preprocess(int root) {
tin.resize(n);
tout.resize(n);
timer = 0;
l = ceil(log2(n));
up.assign(n, vector<int>(l + 1));
dfs(root, root);
}
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findMedian(int _n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
n = _n;
adj.clear();
adj.resize(n);
for(auto& edge : edges) {
adj[edge[0]].push_back({edge[1], edge[2]});
adj[edge[1]].push_back({edge[0], edge[2]});
}
preprocess(0);
vector<long long> rootWeightDist(n), rootDist(n);
[&](this auto&& go, int v, int p, long long cur, int d) -> void {
rootWeightDist[v] = cur, rootDist[v] = d;
for(auto& [ce, w] : adj[v]) {
if(ce == p) continue;
go(ce, v, cur + w, d + 1);
}
}(0, -1, 0, 0);
auto pathSum = [&](int u, int v, int ancestor) -> long long {
return rootWeightDist[u] + rootWeightDist[v] - 2 * rootWeightDist[ancestor];
};
int qSz = queries.size();
vector<int> res(qSz);
for(int i = 0; i < qSz; i++) {
int u = queries[i][0], v = queries[i][1];
int orU = u, orV = v;
if(u == v) {
res[i] = u;
continue;
}
int ancestor = lca(u, v);
long long median = (pathSum(u, v, ancestor) + 1) / 2;
if(pathSum(u, ancestor, ancestor) >= median) {
// somewhere between (u, ancestor) [go up from u to ancestor]
for(int p = 0;; p++) {
int uUp = up[u][p];
if(pathSum(orU, uUp, uUp) >= median) {
// if this is over median, we need to backtrack -1 then go again from p = 0
// this ensures we get the exact front node
// if p is already 0, then `uUp` is the best node
if(p == 0) {
res[i] = uUp;
break;
}else {
u = up[u][p - 1];
p = -1;
}
}
}
}else {
// somewhere between (v, ancestor) [go down from ancestor to v]
// offset is path from (u, ancestor) which we're not accounting for
long long offset = pathSum(u, ancestor, ancestor);
for(int p = 0;; p++) {
int vUp = up[v][p];
// this time, we're going down from ancestor to v
// but we only have up[] so still go up
// once it goes below median, then `vUp` is a bad node
// so backtrack -1 then go again from p = 0
// if p = 0 then `v` is the best node and `vUp` is the "least bad node".
if(pathSum(ancestor, vUp, ancestor) + offset < median) {
if(p == 0) {
break;
}else {
v = up[v][p - 1];
p = -1;
}
}
}
res[i] = v;
}
}
return res;
}
};