Description
Given a weighted undirected connected graph with n vertices numbered from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi, weighti] represents a bidirectional and weighted edge between nodes ai and bi. A minimum spanning tree (MST) is a subset of the graph's edges that connects all vertices without cycles and with the minimum possible total edge weight.
Find all the critical and pseudo-critical edges in the given graph's minimum spanning tree (MST). An MST edge whose deletion from the graph would cause the MST weight to increase is called a critical edge. On the other hand, a pseudo-critical edge is that which can appear in some MSTs but not all.
Note that you can return the indices of the edges in any order.
Example 1:
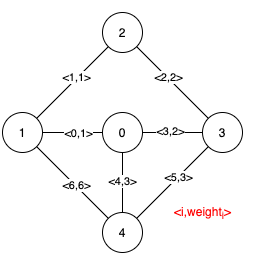
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,2],[0,3,2],[0,4,3],[3,4,3],[1,4,6]] Output: [[0,1],[2,3,4,5]] Explanation: The figure above describes the graph. The following figure shows all the possible MSTs:Notice that the two edges 0 and 1 appear in all MSTs, therefore they are critical edges, so we return them in the first list of the output. The edges 2, 3, 4, and 5 are only part of some MSTs, therefore they are considered pseudo-critical edges. We add them to the second list of the output.
Example 2:
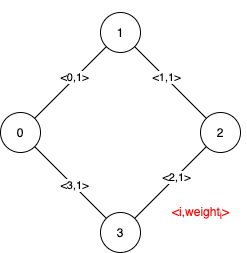
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,1],[0,3,1]] Output: [[],[0,1,2,3]] Explanation: We can observe that since all 4 edges have equal weight, choosing any 3 edges from the given 4 will yield an MST. Therefore all 4 edges are pseudo-critical.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1001 <= edges.length <= min(200, n * (n - 1) / 2)edges[i].length == 30 <= ai < bi < n1 <= weighti <= 1000- All pairs
(ai, bi)are distinct.
Solution
Python3
class UnionFindSet:
def __init__(self, n=0):
self.parents = {}
self.ranks = {}
self.count = 0
for i in range(n):
self.add(i)
def add(self, p):
self.parents[p] = p
self.ranks[p] = 1
self.count += 1
def find(self, u):
if u != self.parents[u]:
self.parents[u] = self.find(self.parents[u])
return self.parents[u]
def union(self, u, v):
pu, pv = self.find(u), self.find(v)
if pu == pv:
return False
if self.ranks[pu] < self.ranks[pv]:
self.parents[pu] = pv
elif self.ranks[pu] > self.ranks[pv]:
self.parents[pv] = pu
else:
self.parents[pv] = pu
self.ranks[pu] += 1
self.count -= 1
return True
# UnionFind + Kruskal + Enumerate edges
# O(ElogE + E^2 + E^2)
class Solution:
def findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
# sort edges in asc order based on weight
edges = [(u, v, w, i) for i, (u, v, w) in enumerate(edges)]
edges.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
# do not use this edge
def find_mst_without_this_edge(edge_idx):
union_find_set = UnionFindSet(n)
ans = 0
for i, (u, v, w, _) in enumerate(edges):
# do not use this edge
if i == edge_idx:
continue
if union_find_set.union(u, v):
ans += w
parent = union_find_set.find(0)
return ans if all(union_find_set.find(i) == parent for i in range(n)) else inf
# need to use this edge
def find_mst_with_this_edge(edge_idx):
union_find_set = UnionFindSet(n)
# use this edge first
u0, v0, w0, _ = edges[edge_idx]
ans = w0
union_find_set.union(u0, v0)
for i, (u, v, w, _) in enumerate(edges):
# do not use this edge
if i == edge_idx:
continue
if union_find_set.union(u, v):
ans += w
parent = union_find_set.find(0)
return ans if all(union_find_set.find(i) == parent for i in range(n)) else inf
# normal MST total weight
base = find_mst_without_this_edge(-1)
cri, p_cri = set(), set()
for i in range(len(edges)):
wgt_excl = find_mst_without_this_edge(i)
# if not included, MST total weight would increase
if wgt_excl > base:
cri.add(edges[i][3])
else:
wgt_incl = find_mst_with_this_edge(i)
# with this edge, MST total weight doesn't change
if wgt_incl == base:
p_cri.add(edges[i][3])
return [cri, p_cri]