Description
You are given the root of a full binary tree with the following properties:
- Leaf nodes have either the value
0or1, where0representsFalseand1representsTrue. - Non-leaf nodes have either the value
2or3, where2represents the booleanORand3represents the booleanAND.
The evaluation of a node is as follows:
- If the node is a leaf node, the evaluation is the value of the node, i.e.
TrueorFalse. - Otherwise, evaluate the node's two children and apply the boolean operation of its value with the children's evaluations.
Return the boolean result of evaluating the root node.
A full binary tree is a binary tree where each node has either 0 or 2 children.
A leaf node is a node that has zero children.
Example 1:
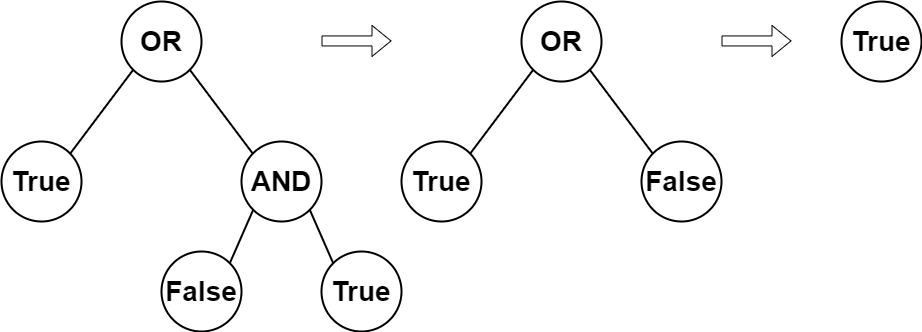
Input: root = [2,1,3,null,null,0,1] Output: true Explanation: The above diagram illustrates the evaluation process. The AND node evaluates to False AND True = False. The OR node evaluates to True OR False = True. The root node evaluates to True, so we return true.
Example 2:
Input: root = [0] Output: false Explanation: The root node is a leaf node and it evaluates to false, so we return false.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 3- Every node has either
0or2children. - Leaf nodes have a value of
0or1. - Non-leaf nodes have a value of
2or3.
Solution
Python3
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def evaluateTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
def dfs(node):
if not node.left and not node.right: return node.val
if node.val == 2:
return dfs(node.left) or dfs(node.right)
else:
return dfs(node.left) and dfs(node.right)
return dfs(root)