Description
There are numBottles water bottles that are initially full of water. You can exchange numExchange empty water bottles from the market with one full water bottle.
The operation of drinking a full water bottle turns it into an empty bottle.
Given the two integers numBottles and numExchange, return the maximum number of water bottles you can drink.
Example 1:
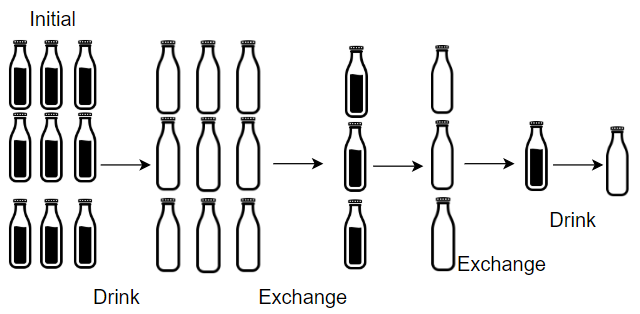
Input: numBottles = 9, numExchange = 3 Output: 13 Explanation: You can exchange 3 empty bottles to get 1 full water bottle. Number of water bottles you can drink: 9 + 3 + 1 = 13.
Example 2:
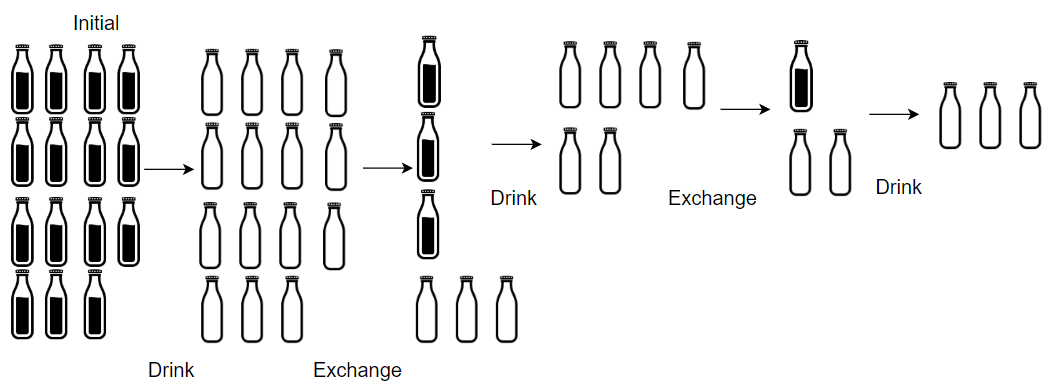
Input: numBottles = 15, numExchange = 4 Output: 19 Explanation: You can exchange 4 empty bottles to get 1 full water bottle. Number of water bottles you can drink: 15 + 3 + 1 = 19.
Constraints:
1 <= numBottles <= 1002 <= numExchange <= 100
Solution
Python3
class Solution:
def numWaterBottles(self, numBottles: int, numExchange: int) -> int:
res = numBottles
while numBottles >= numExchange:
numBottles, rem = divmod(numBottles, numExchange)
res += numBottles
numBottles += rem
return resC++
class Solution {
public:
int numWaterBottles(int numBottles, int numExchange) {
int res = numBottles;
while (numBottles >= numExchange){
int remaining = numBottles % numExchange;
numBottles /= numExchange;
res += numBottles;
numBottles += remaining;
}
return res;
}
};