Description
Given an integer array num sorted in non-decreasing order.
You can perform the following operation any number of times:
- Choose two indices,
iandj, wherenums[i] < nums[j]. - Then, remove the elements at indices
iandjfromnums. The remaining elements retain their original order, and the array is re-indexed.
Return the minimum length of nums after applying the operation zero or more times.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: 0
Explanation:
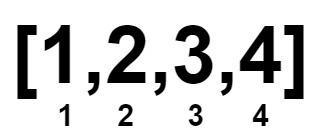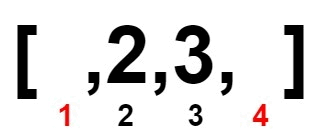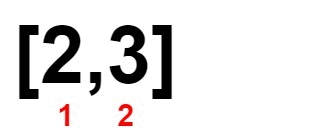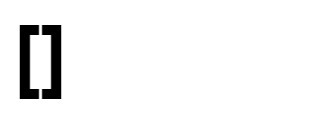
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,2,2,3,3]
Output: 0
Explanation:
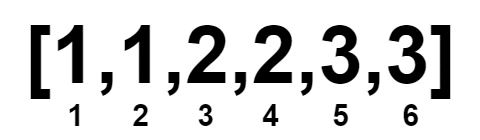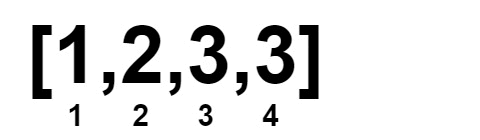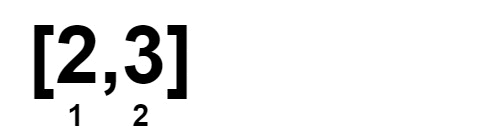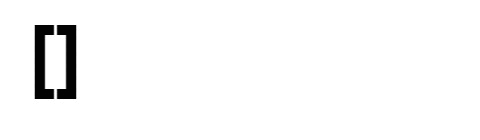
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1000000000,1000000000]
Output: 2
Explanation:
Since both numbers are equal, they cannot be removed.
Example 4:
Input: nums = [2,3,4,4,4]
Output: 1
Explanation:
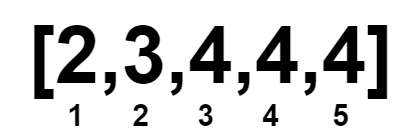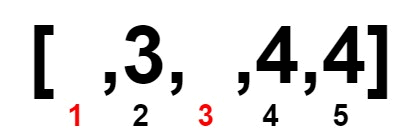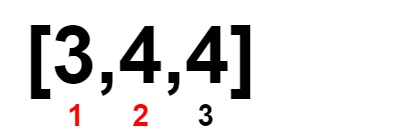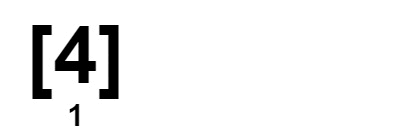
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 109numsis sorted in non-decreasing order.
Solution
Python3
class Solution:
def minLengthAfterRemovals(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
N = len(nums)
counter = Counter(nums)
pq = [-v for v in counter.values()]
heapify(pq)
while len(pq) >= 2:
top = -heappop(pq)
second = -heappop(pq)
top -= 1
second -= 1
if top > 0:
heappush(pq, -top)
if second > 0:
heappush(pq, -second)
return sum(-v for v in pq)