Description
You are given a 2D matrix grid of size m x n. In one operation, you can change the value of any cell to any non-negative number. You need to perform some operations such that each cell grid[i][j] is:
- Equal to the cell below it, i.e.
grid[i][j] == grid[i + 1][j](if it exists). - Different from the cell to its right, i.e.
grid[i][j] != grid[i][j + 1](if it exists).
Return the minimum number of operations needed.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[1,0,2],[1,0,2]]
Output: 0
Explanation:
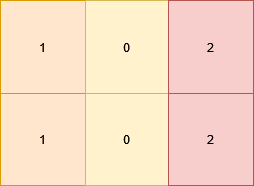
All the cells in the matrix already satisfy the properties.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,1,1],[0,0,0]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
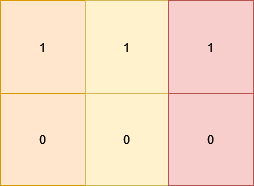
The matrix becomes [[1,0,1],[1,0,1]] which satisfies the properties, by doing these 3 operations:
- Change
grid[1][0]to 1. - Change
grid[0][1]to 0. - Change
grid[1][2]to 1.
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1],[2],[3]]
Output: 2
Explanation:

There is a single column. We can change the value to 1 in each cell using 2 operations.
Constraints:
1 <= n, m <= 10000 <= grid[i][j] <= 9
Solution
Python3
class Solution:
def minimumOperations(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
rows, cols = len(grid), len(grid[0])
counterCol = [[0] * 10 for _ in range(cols)]
for c, col in enumerate(zip(*grid)):
for v in col:
counterCol[c][v] += 1
@cache
def go(j, last):
if j == cols: return 0
res = inf
for k in range(10):
# means the k has been used already
if last == k: continue
# change the current column to k
res = min(res, go(j + 1, k) + (rows - counterCol[j][k]))
return res
return go(0, -1)