Description
You are given the root of a binary tree.
A ZigZag path for a binary tree is defined as follow:
- Choose any node in the binary tree and a direction (right or left).
- If the current direction is right, move to the right child of the current node; otherwise, move to the left child.
- Change the direction from right to left or from left to right.
- Repeat the second and third steps until you can't move in the tree.
Zigzag length is defined as the number of nodes visited - 1. (A single node has a length of 0).
Return the longest ZigZag path contained in that tree.
Example 1:
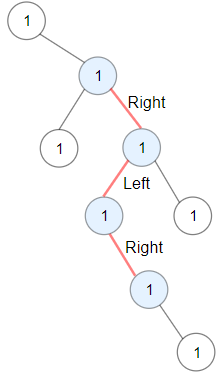
Input: root = [1,null,1,1,1,null,null,1,1,null,1,null,null,null,1] Output: 3 Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (right -> left -> right).
Example 2:
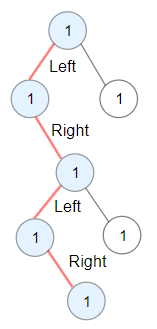
Input: root = [1,1,1,null,1,null,null,1,1,null,1] Output: 4 Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (left -> right -> left -> right).
Example 3:
Input: root = [1] Output: 0
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 5 * 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution
Python3
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def longestZigZag(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
res = 0
def go(node, depth, isLeft):
nonlocal res
res = max(res, depth)
if not node: return
go(node.left, depth + 1 if not isLeft else 0, True)
go(node.right, depth + 1 if isLeft else 0, False)
go(root.left, 0, True)
go(root.right, 0, False)
return res