Description
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1,3,4]
Explanation:
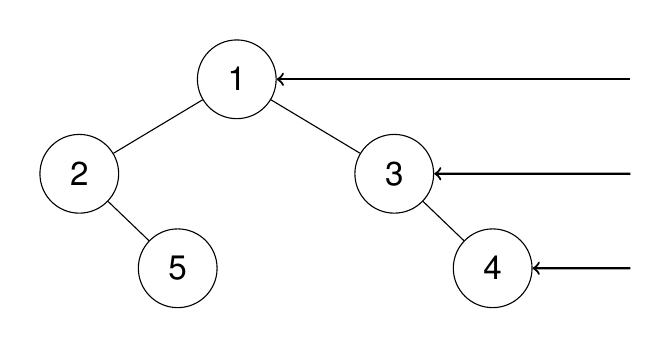
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,null,null,5]
Output: [1,3,4,5]
Explanation:

Example 3:
Input: root = [1,null,3]
Output: [1,3]
Example 4:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution
Python3
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
if not root: return []
res = []
queue = deque([root])
while queue:
N = len(queue)
for _ in range(N):
node = queue.popleft()
for leaf in filter(None, (node.left, node.right)):
queue.append(leaf)
res.append(node.val)
return res